
Meltio, an international manufacturer of metal 3D solutions based in Spain and the US, has announced that it is launching four new materials, Stainless Steel 17-4PH, Tool Steel H11, Nickel 625 and Invar, as part of its metal wire materials range. These materials have been designed to help their users to expand applications as they have been optimized for use with Meltio solutions. The move not only shows the maturity of Meltio’s own LMD technology, but also is expected to help push adoption of metal 3D printing through Meltio’s cost-effective products by allowing for less guessing when it comes to printer parameters.
Earlier this year Meltio released its first launch of materials. These were designed to be optimized for use with Meltio’s own solutions namely the Meltio M450 3D printer, the Meltio Engine CNC Integration and the Meltio Engine Robotic Integration, products which have already been adopted by major players in industry including Phillips Corporation. Though the company has kept an open material system, ensuring that users do not need to use their materials to have excellent results, Meltio’s own materials have been extensively tested under controlled conditions. They are intended to provide users with materials that have validated part properties and optimized print parameters. The first round centered on common metals used with Meltio’s technology namely Stainless Steel 316L, Stainless Steel 308L, Mild Steel ER70S, Titanium 64 and Nickel 718. Now with this latest release the company aims to cater to an even broader audience as well as allowing for more niche applications.
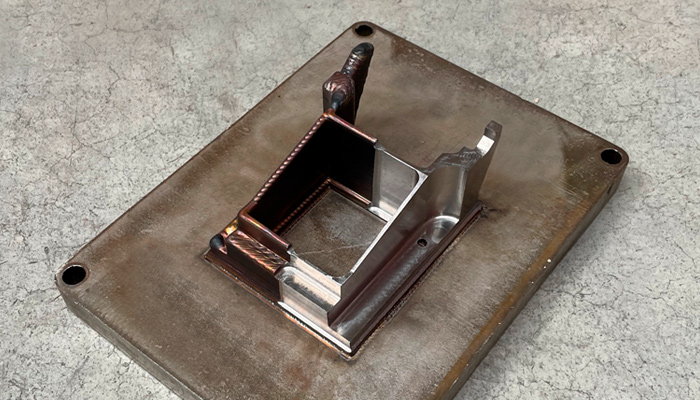

Meltio has maintained an open materials system to drive the adoption of the technology.
For the development of materials, Meltio has focused on metal wire since its systems use a technology called laser metal deposition (LMD). LMD is a Directed Energy Deposition (DED) process, meaning that a focused energy source, in this case, multiple lasers are used to melt the deposited material as it goes through the nozzle, often wires. It has been gaining in popularity over the past few years thanks to its flexibility as well as the benefits of using wires over powder. Notably, they are safer, cleaner and easier to work with than many powders, plus they are often considered to be sustainable, a benefit when you consider that additive manufacturing in general is being posited as a way to help address growing environmental concerns.
What to Expect From Meltio’s New Materials
The choice to develop these four materials in particular was determined by user interest as Meltio chose those most demanded by their customer base. The drive, of course, centered on the fact that these specially developed materials have been perfectly optimized for use on Meltio solutions. This means that by turning to the optimized print profiles (which not only reduce the possibility of print failures but also makes printing easier, giving even beginners access to the technology), users are able to have guaranteed part properties, a critical need in industries with high requirements.
Indeed, out of the four materials chosen, three are ideal for applications in aerospace. Meltio SS17-4PH has much higher hardness than previous offerings as well as excellent corrosion resistance and mechanical properties. It is a commonly used stainless steel and would allow users to turn to additive manufacturing in the oil & gas, aerospace, energy and defense industries. Meanwhile, Meltio ToolSteelH11 is a chromium-based steel used for tool steels thanks to its impact toughness. It is often used for hot tooling as well as for aerospace applications. Meltio Invar is also ideal for use in aerospace. This is because it has an extremely low coefficient of expansion, from -250°C up to about 200°C. In layman terms, this means that it will not expand when heated making it an appropriate choice for high-temperature applications including aerospace of course but also measuring equipment and molds.
This new range of materials is particularly interesting for industries with high requirements, such as aerospace.
Last but not least, the final material released by Meltio is the Meltio Nickel 625. According to Meltio, this is a nickel-based superalloy which was chosen thanks to its excellent mechanical properties at a wide range of temperatures. However, it is particularly adept for its weldability. This is especially important for a DED solution as this material is very useful for repairing components that work at high temperatures or need increased corrosion protection. Considering that one of the main benefits of using this particular additive manufacturing technology is its usefulness when it comes to part repair, the addition makes sense as a way to fulfill Meltio’s goal to increase applications and uses for its users.
What Will Be Next?
For now, it seems that Meltio is looking into further material expansion for its proprietary systems. This is because the company believes that by maintaining an open material platform while also having its own Meltio Materials range, that users will be able to benefit from both, showing as well the maturity of its own wire LMD technology. Additionally, having their own wire materials will help facilitate adoption of metal 3D printing in a cost-effective and efficient way. Ángel Llavero, Meltio’s CEO, added: “With the launch of this new batch of Meltio Materials, we would like to reinforce our position as the leading OEM in the DED space that pledges for the use of welding wire over powder because of its numerous advantages. Our plan is to keep broadening our selection according to our users’ demands while keeping an open materials platform for those who would like to push the envelope and experiment with different materials”. You can learn more about this launch HERE.
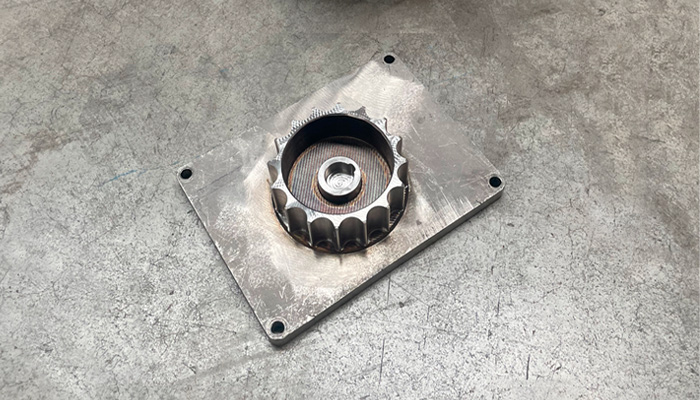

These new materials demonstrate the maturity of metal additive manufacturing.
*All photo credits: Meltio
Original



